Tkinter filedialog askopenfilename Options
File dialog in Tkinter allows users to navigate their file system and select files for their application to process.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to customize filedialog.askopenfilename dialog title, set initial directories, specify file types, and much more.
Customize the Dialog Title
You can set the filedialog.askopenfilename title using the title option:
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import filedialog root = tk.Tk() root.withdraw() file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(title="Select a File") print(file_path)
Code Output:
/Users/likegeeks/Documents/sample.csv
Set the Initial Directory
You can set the initial directory using initialdir option:
import os
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
initial_dir = os.path.expanduser("~/Documents")
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(initialdir=initial_dir, title="Select a File")
print(file_path)
Code Output:
/Users/likegeeks/Documents/datafile.csv
In this code, os.path.expanduser("~/Documents") is used to set the initial directory.
This method is cross-platform, meaning it works on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
~/Documents is a relative path, which expanduser converts into an absolute path.
Specify Initial File Selection
The initialfile option in filedialog.askopenfilename allows you to pre-select a file when the dialog opens.
This is useful when you expect the user to frequently choose a specific file or type of file.
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import filedialog root = tk.Tk() root.withdraw() initial_file = "example.csv" file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(initialfile=initial_file, title="Select a File") print(file_path)
Code Output:
/Users/likegeeks/Documents/example.csv
In this snippet, initialfile is set to "example.csv". When the file dialog opens, it automatically highlights example.csv if it exists in the current directory.
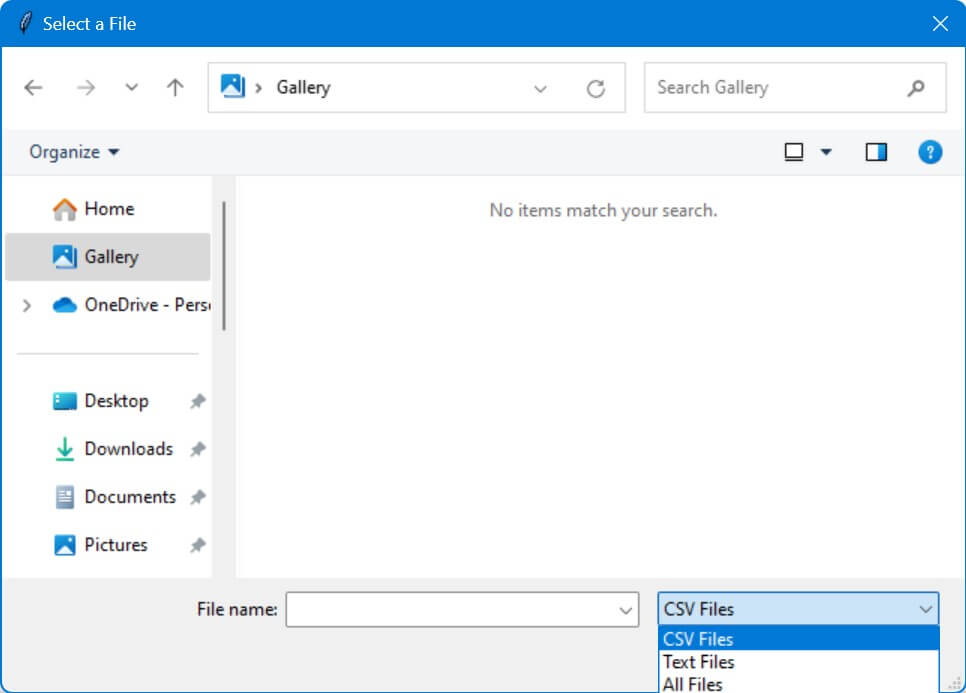
Specify File Types
You can pass a list of tuples where each tuple contains a descriptive string and a file pattern to filetypes option to restrict the file dialog to show only specific types of files.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
file_types = [("CSV Files", "*.csv"), ("Text Files", "*.txt"), ("All Files", "*.*")]
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(filetypes=file_types, title="Select a File")
print(file_path)
Code Output:
/Users/likegeeks/Documents/datafile.csv
The filetypes option allows you to select CSV files, text files, and any other file type.
Implement Default File Extensions
You can use the defaultextension option to automatically append a specified extension to the file name if the user does not provide one.
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import filedialog root = tk.Tk() root.withdraw() file_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(defaultextension=".csv", title="Save File") print(file_path)
Code Output:
/Users/likegeeks/Documents/untitled.csv
Here, defaultextension=".csv" ensures that any file saved through this dialog will end with “.csv” if no other extension is specified by the user.
Designating a Parent Window (Always On Top)
By setting a parent window using the parent option, the file dialog is tied to a specific part of your application.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Main Application Window")
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(parent=root, title="Select a File")
print(file_path)
Code Output:
/Users/likegeeks/Documents/selectedfile.csv
This ensures that the file dialog is always on top of the parent window and moves with it.
Typevariable Option Usage
Using the typevariable option in Tkinter filedialog.askopenfilename allows you to dynamically link the selected file types to other UI elements in your application.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog, StringVar
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
file_type_var = StringVar()
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(typevariable=file_type_var, title="Select a File")
print("Selected File Path:", file_path)
print("Selected File Type:", file_type_var.get())
Code Output:
Selected File Path: /Users/likegeeks/Documents/datafile.csv Selected File Type: .csv
In this example, a StringVar named file_type_var is used.
This variable is linked to the typevariable option in the file dialog.
When a file is selected, file_type_var captures the file extension of the selected file.
Auto-add Extensions
The addextension option in Tkinter filedialog.askopenfilename ensures that files are saved with the correct extension automatically.
This functionality is useful when the user forgets to specify an extension.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
file_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(addextension=True, filetypes=[("CSV Files", "*.csv"), ("Text Files", "*.txt")], defaultextension=".csv", title="Save File")
print(file_path)
Code Output:
/Users/likegeeks/Documents/MyData.csv
Here, addextension=True ensures that if the user does not specify an extension, the file dialog automatically adds it based on the defaultextension or the selected file type.
In the provided code, if a user saves a file named “MyData” without specifying an extension, the dialog automatically appends “.csv” to the file name.
Restrict to Existing Files
The mustexist option in Tkinter filedialog.askopenfilename ensures that users can only select files that actually exist.
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import filedialog root = tk.Tk() root.withdraw() file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(mustexist=True, title="Select an Existing File") print(file_path)
Code Output:
/Users/likegeeks/Documents/existingfile.csv
In this code, the mustexist=True argument restricts the file dialog to only allow the selection of files that exist on the file system.
If a user tries to enter a non-existent file name manually, the dialog will prompt them to select an existing file.
Mokhtar is the founder of LikeGeeks.com. He is a seasoned technologist and accomplished author, with expertise in Linux system administration and Python development. Since 2010, Mokhtar has built an impressive career, transitioning from system administration to Python development in 2015. His work spans large corporations to freelance clients around the globe. Alongside his technical work, Mokhtar has authored some insightful books in his field. Known for his innovative solutions, meticulous attention to detail, and high-quality work, Mokhtar continually seeks new challenges within the dynamic field of technology.