6 Methods To Add & Update Items In Tkinter Combobox
In this tutorial, you’ll learn various methods to add or update items in Tkinter Combobox.
We’ll cover direct initialization, using the set & configure methods, adding items at specific positions, and avoiding duplicates.
Direct Initialization at Creation
Here’s a simple code example:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
root = tk.Tk()
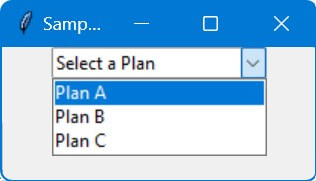
root.title("Sample Combobox")
sample_data = ["Plan A", "Plan B", "Plan C"]
# Creating the Combobox and adding items directly
combobox = ttk.Combobox(root, values=sample_data)
combobox.pack()
combobox.set("Select a Plan")
root.mainloop()
Code Output:
The values parameter in the ttk.Combobox constructor is where you directly input your list of options.
In this case, sample_data represents possible choices.
Using the set Method (Append Items)
Sometimes, you need to dynamically add a single item or modify the entire list of items in a Tkinter Combobox after it has already been created.
You can do this using the set method.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
# Function to update the Combobox
def update_combobox(new_data, add_single_item=False):
if add_single_item:
current_values = list(combobox['values'])
current_values.append(new_data)
combobox['values'] = current_values
else:
combobox['values'] = new_data
root = tk.Tk()
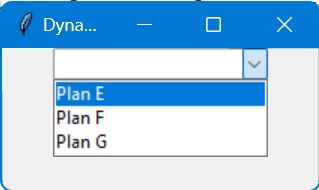
root.title("Dynamic Combobox Update")
combobox = ttk.Combobox(root)
combobox.pack()
new_plan = "Plan D"
new_plan_list = ["Plan E", "Plan F", "Plan G"]
# Update Combobox with a single item
update_combobox(new_plan, add_single_item=True)
# Update Combobox with a new list of items
update_combobox(new_plan_list)
root.mainloop()
Code Output:
In this code, we define a function update_combobox that takes new data and a flag add_single_item.
If add_single_item is True, the function adds a single item to the existing list.
If False, it replaces the current list with a new one.
In the above code, we replaced the list with new items.
Using configure Method
The configure method in Tkinter allows you to either add a single item or update the entire list of items in a Combobox after it’s been created.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
def update_combobox_config(new_data, add_single_item=False):
if add_single_item:
current_values = list(combobox['values'])
current_values.append(new_data)
combobox.configure(values=current_values)
else:
combobox.configure(values=new_data)
root = tk.Tk()
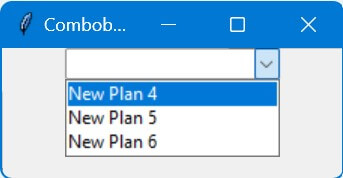
root.title("Combobox Update with configure")
combobox = ttk.Combobox(root, values=["Initial Plan 1", "Initial Plan 2"])
combobox.pack()
additional_plan = "Additional Plan 3"
new_plan_list = ["New Plan 4", "New Plan 5", "New Plan 6"]
# Update Combobox with a single item
update_combobox_config(additional_plan, add_single_item=True)
# Update Combobox with a new list of items
update_combobox_config(new_plan_list)
root.mainloop()
Code Output:
The update_combobox_config function, like in the previous example, either appends a single item or replaces the entire list based on the add_single_item flag.
Add Items at the Beginning
You can use the configure method to add items to Tkinter combobox at the beginning.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
root = tk.Tk()
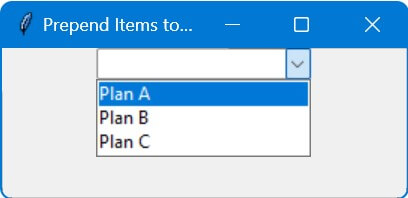
root.title("Prepend Items to Combobox")
initial_data = ["Plan B", "Plan C"]
combobox = ttk.Combobox(root, values=initial_data)
combobox.pack()
def add_items_at_beginning(new_items):
current_values = list(combobox['values'])
combobox['values'] = new_items + current_values
new_items = ["Plan A"]
add_items_at_beginning(new_items)
root.mainloop()
Code Output:
The add_items_at_beginning function takes a list of new items and concatenates them with the current list in the Combobox.
The combobox['values'] = new_items + current_values combines the new items with the existing ones.
Add Items at the End
You can use the configure method to append items to Tkinter combobox at the end.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Append Items to Combobox")
initial_data = ["Plan A", "Plan B"]
combobox = ttk.Combobox(root, values=initial_data)
combobox.pack()
def add_items_at_end(new_items):
current_values = list(combobox['values'])
combobox['values'] = current_values + new_items
new_items = ["Plan C", "Plan D"]
add_items_at_end(new_items)
root.mainloop()
Code Output:
The add_items_at_end function takes the new items and appends them to the existing list of values in the Combobox.
The combobox['values'] = current_values + new_items line appends the new items to the end of the list.
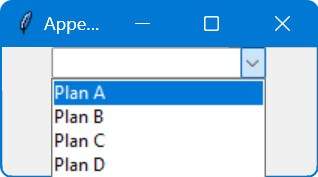
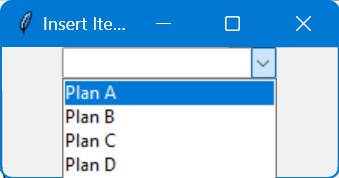
Insert Items at a Specific Position
You can use the insert method on the list of Tkinter combobox current values to place the new item at the specified index.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Insert Items at Specific Position")
initial_data = ["Plan A", "Plan C", "Plan D"]
combobox = ttk.Combobox(root, values=initial_data)
combobox.pack()
def insert_item(position, new_item):
current_values = list(combobox['values'])
current_values.insert(position, new_item)
combobox['values'] = current_values
new_item = "Plan B"
insert_item(1, new_item)
root.mainloop()
Code Output:
The insert_item function takes the desired position and the new item as arguments.
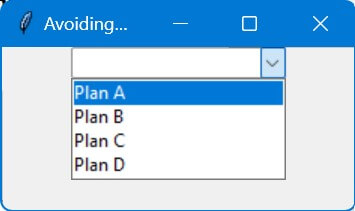
Avoid Duplicates when Adding Items
You can use a simple if statement to check if the item you want to add is not in the Tkinter combobox values.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Avoiding Duplicates in Combobox")
initial_data = ["Plan A", "Plan B", "Plan C"]
combobox = ttk.Combobox(root, values=initial_data)
combobox.pack()
def add_if_not_duplicate(new_item):
current_values = list(combobox['values'])
if new_item not in current_values:
current_values.append(new_item)
combobox['values'] = current_values
new_items = ["Plan B", "Plan D"]
for item in new_items:
add_if_not_duplicate(item)
root.mainloop()
Code Output:
The add_if_not_duplicate function checks whether the new item is already in the Combobox’s list.
If it’s not, the item is appended.
Mokhtar is the founder of LikeGeeks.com. He is a seasoned technologist and accomplished author, with expertise in Linux system administration and Python development. Since 2010, Mokhtar has built an impressive career, transitioning from system administration to Python development in 2015. His work spans large corporations to freelance clients around the globe. Alongside his technical work, Mokhtar has authored some insightful books in his field. Known for his innovative solutions, meticulous attention to detail, and high-quality work, Mokhtar continually seeks new challenges within the dynamic field of technology.