20 Main Linux commands that you will need daily
In the previous post, we discussed how to install Linux; now, we are going to talk about the most powerful features in Linux, which are Linux commands or shell commands.
For the complete documentation of Linux Commands, you can check Linux Documentation.
The power of Linux is in the power of commands that you can use.
I’m going to talk about the main Linux commands with their main parameters that you might use daily.
- 1 ls command
- 2 cd command
- 3 cp command
- 4 mv command
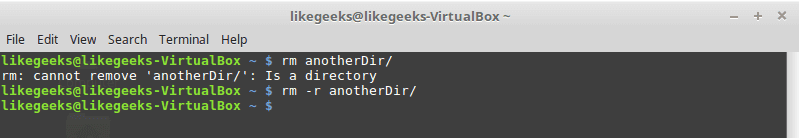
- 5 rm command
- 6 mkdir command
- 7 rmdir command
- 8 chown command
- 9 chmod command
- 10 locate command
- 11 updatedb command
- 12 date command
- 13 tar command
- 14 cat command
- 15 less command
- 16 grep command
- 17 passwd command
- 18 du command
- 19 reboot command
- 20 halt command
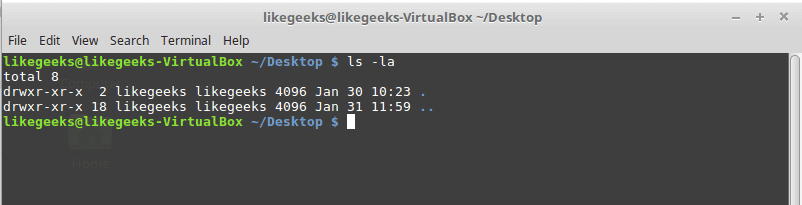
ls command
List files and folders in the current directory.
Parameters
–l
to list the content as a detailed list.
-a
Display all files (hidden + non-hidden).
You can combine parameters like this:
ls -la
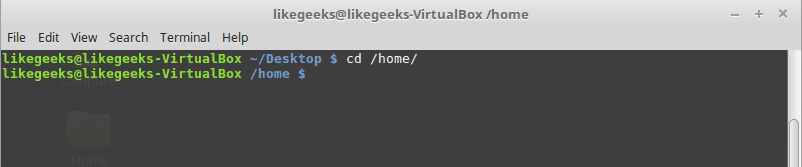
cd command
Change directory from the current directory to another one.
cd /home
Will go to the home directory
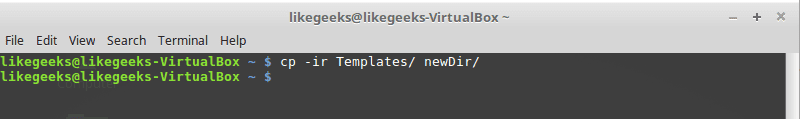
cp command
Copy the source to target.
Parameters
-i
Interactive mode means waiting for the confirmation if there are files on the target, it will be overwritten.
-r
Recursive copy means include subdirectories if they found.
Example
cp –ir sourcedir targetdir
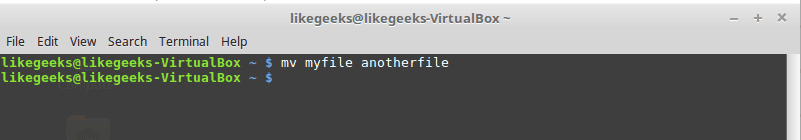
mv command
Move the source to target and remove the source.
Parameters
-i
Interactive mode means to wait for the confirmation if there are files on the target, it will be overwritten.
Example
mv –i sourceFile targetFile
rm command
Delete file or directory, and you must use –r in case you want to delete a directory.
Parameters
-r
Recursive delete means delete all subdirectories if found.
-i
Interactive means wait till confirmation
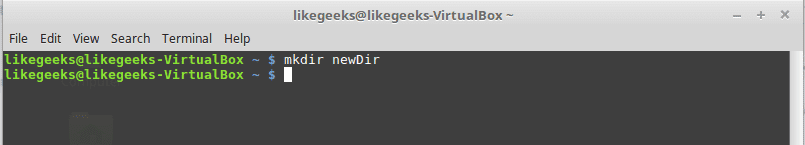
mkdir command
Create a new directory.
mkdir newDir
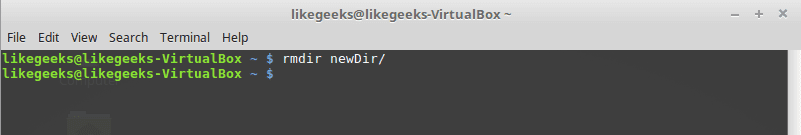
rmdir command
Delete a directory
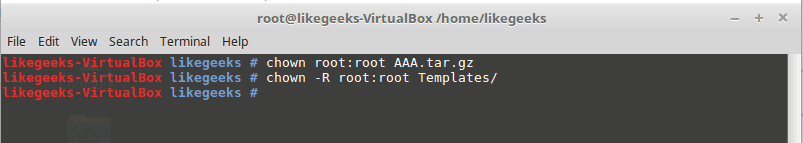
chown command
Change the owner of a file or directory.
Parameters:
-R
Capital R here means to change ownership of all subdirectories if found, and you must use this parameter if you use the command against a directory.
chown –R root:root myDir
chmod command
Change the permission of a file or directory.
Parameters
The mode which consists of 3 parts, owner, group, and others means what will be the permissions for these modes, and you must specify them.
The permission is one of the followings:
Read =4
Write = 2
Execute =1
Every permission represented by a number as shown, and you can combine permissions.
Example
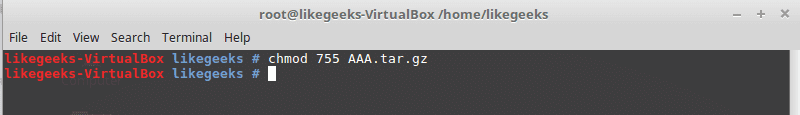
chmod 755 myfile
That means set permission for the file named myfile as follows:
owner: set it to 7, which means 4+2+1 means read+write+execute.
group: set it to 5, which means 4+1 means read+execute.
other: set it to 5, which means 4+1 means read+execute.
Note: execute for a folder, means opening it.
locate command
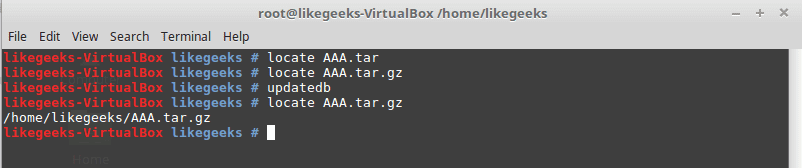
To find a file in your system, the locate command will search the system for the pattern you provide.
locate myfile
updatedb command
updates the database used by the locate command.
date command
Simply prints today’s date. Just type date on the shell.
tar command
Combines several files into an archive and compression if you want.
Parameters
-c
Create a new archive.
-z
Compress the archive using gzip package.
-j
Compress the archive using the bzip2 package.
-v
Verbose mode means showing the processed files.
-f
Write the output to a file and not to screen.
-x
Unpack files from an archive.
Example
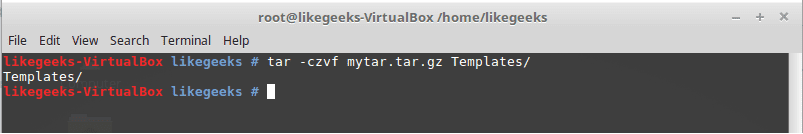
tar –czvf myfiles.tar.gz myfiles
This command will pack and compress all files in folder myfiles to a compressed archive named myfiles.tar.gz.
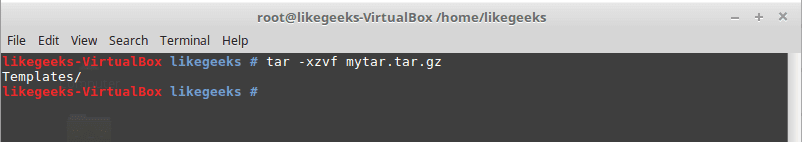
tar-xzvf myfiels.tar.gz
This command will decompress the archive.
cat command
Display file content to screen without limits.
Example
cat myfile.txt
less command
Displays file content with a scroll screen so you can navigate between pages using PgUp, PgDn, Home, and End.
less myfile
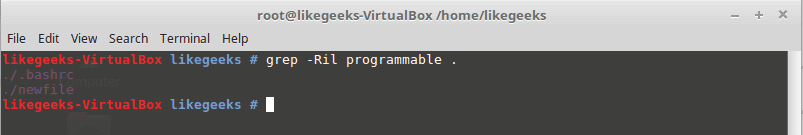
grep command
Searches for a string in the specified files and displays which line contains the matched string.
Parameters
-R
Recursive search inside subdirectories if found.
-i
Insensitive search and ignore case.
-l
Displays file name, not the text lines.
Example
grep –Ril mystring /home
passwd command
Used to change your user password.
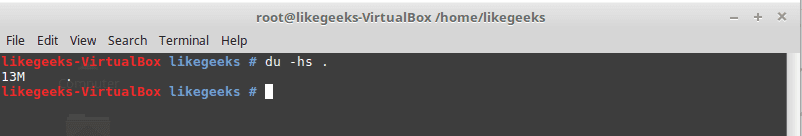
du command
Calculates the disk usage of a file or a directory.
Parameters
-h
Display human-readable form.
-s
Summarize the output total size.
Example
du –hs /home
reboot command
Reboot the system immediately. Just type reboot.
halt command
Shuts down the system, but make sure to close all of your files to avoid data loss.
That was just some of the leading Linux commands.
Notice that, if you forget any command parameters, just type the command with – -help as a parameter, and it will list the used parameters, so you don’t have to remember all those parameters at the beginning.
cat --help
To be continued.
Mokhtar is the founder of LikeGeeks.com. He is a seasoned technologist and accomplished author, with expertise in Linux system administration and Python development. Since 2010, Mokhtar has built an impressive career, transitioning from system administration to Python development in 2015. His work spans large corporations to freelance clients around the globe. Alongside his technical work, Mokhtar has authored some insightful books in his field. Known for his innovative solutions, meticulous attention to detail, and high-quality work, Mokhtar continually seeks new challenges within the dynamic field of technology.


nice well explained for a beginer
Thanks Gordon!
Really helpful !
Thanks a lot!
Very helpful. Thanks.
You’re welcome. Thanks!