Create 3D Plots Using IPyvolume in Jupyter Notebooks
IPyvolume is a powerful Python library for creating interactive 3D plots in Jupyter Notebooks.
This tutorial will guide you through creating various types of 3D plots using IPyvolume, from simple scatter plots to complex volume renderings.
To get started, install IPyvolume and import the necessary libraries:
!pip install ipyvolume import ipyvolume as ipv import numpy as np
Scatter Plot
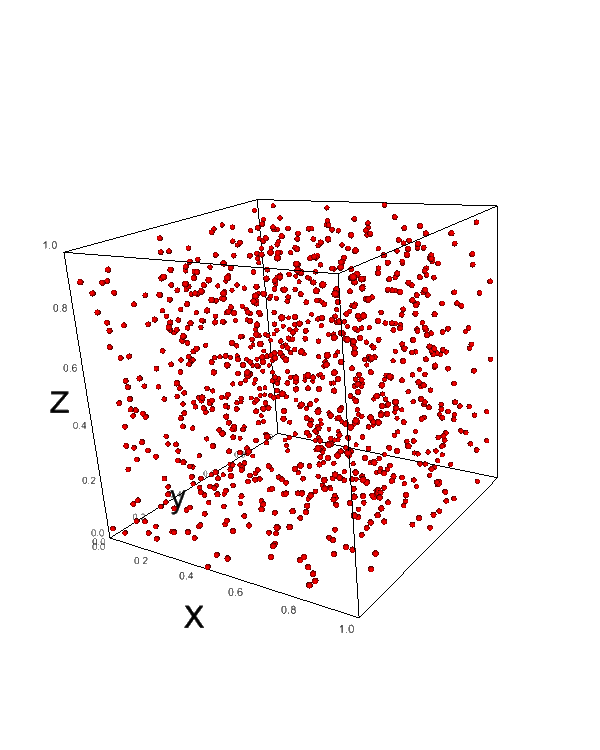
To create a 3D scatter plot, use the ipv.scatter() function:
x = np.random.random(1000) y = np.random.random(1000) z = np.random.random(1000) fig = ipv.figure() ipv.scatter(x, y, z, marker='sphere') ipv.show()
Output:
This code generates a 3D scatter plot with 1000 randomly distributed points.
The marker='sphere' parameter sets the point style to spheres.
Line Plot
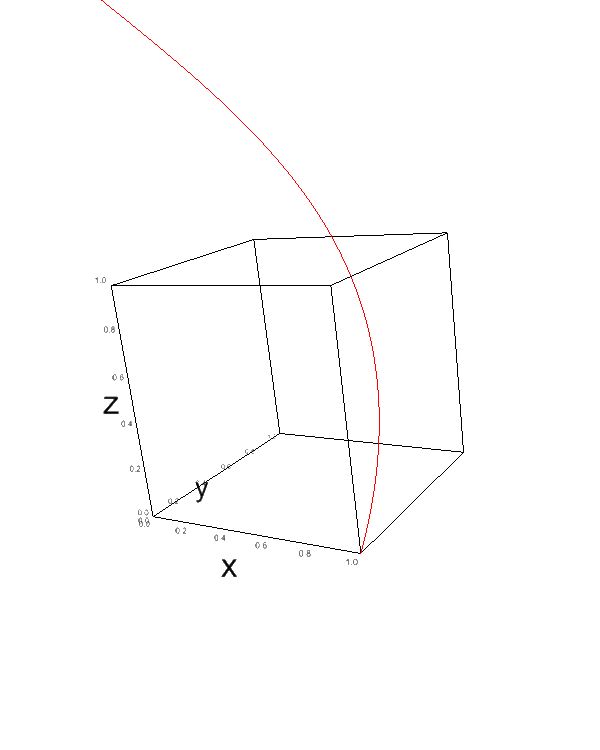
To create a 3D line plot, you can use the ipv.plot() function:
t = np.linspace(0, 10, 1000) x = np.cos(t) y = np.sin(t) z = t fig = ipv.figure() ipv.plot(x, y, z) ipv.show()
Output:
This code produces a 3D spiral line plot.
The t variable represents time, and x, y, and z are parametric equations for the spiral.
Surface Plot
To create a 3D surface plot, use the ipv.plot_surface() function:
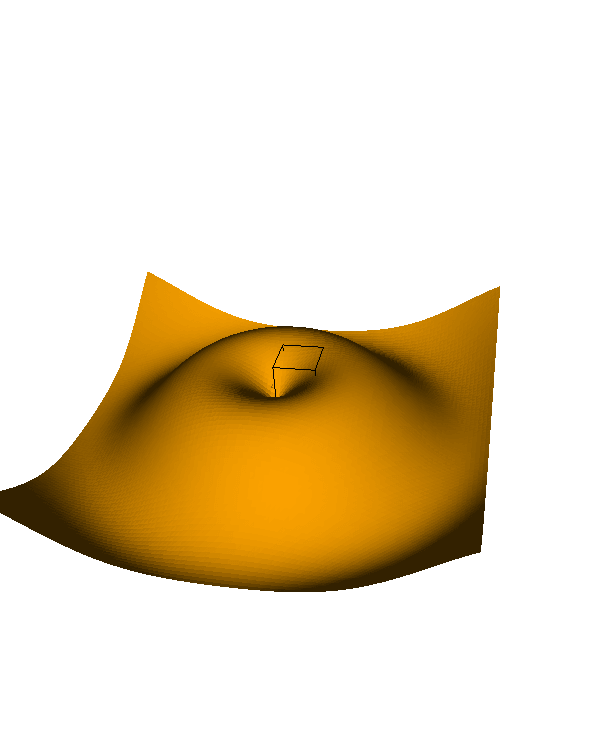
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100) y = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100) x, y = np.meshgrid(x, y) z = np.sin(np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2)) fig = ipv.figure() ipv.plot_surface(x, y, z, color='orange') ipv.show()
Output:
This code creates a 3D surface plot of a sinc function.
The np.meshgrid() function generates a 2D grid of x and y values, and z is calculated using these values.
Wireframe Plot
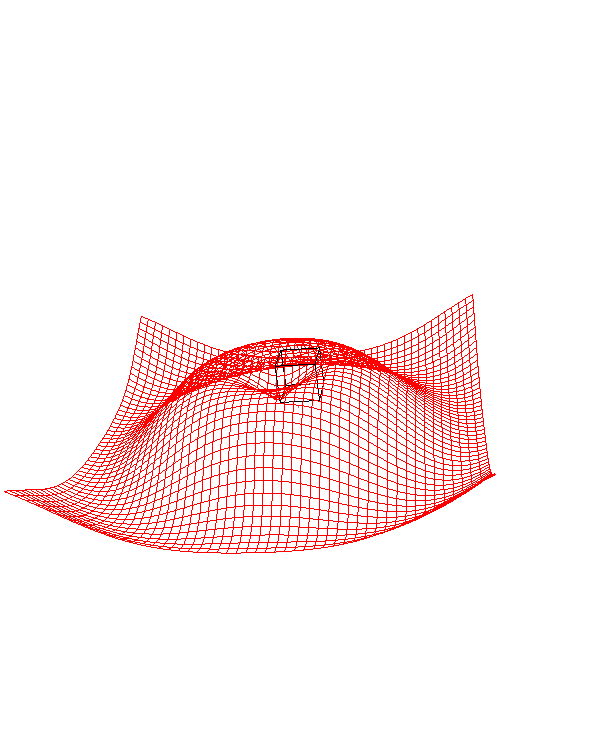
To create a wireframe plot, use the ipv.plot_wireframe() function:
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 50) y = np.linspace(-5, 5, 50) x, y = np.meshgrid(x, y) z = np.sin(np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2)) fig = ipv.figure() ipv.plot_wireframe(x, y, z) ipv.show()
Output:
This code generates a wireframe representation of the same sinc function used in the surface plot example.
Quiver Plot (Vector Fields)
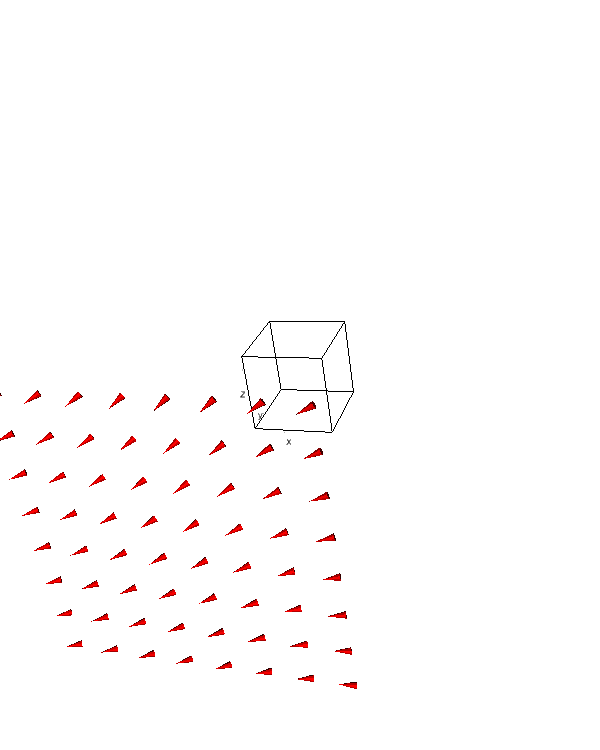
To create a quiver plot for visualizing vector fields, use the ipv.quiver() function:
x, y, z = np.meshgrid(np.arange(-2, 2, 0.5),
np.arange(-2, 2, 0.5),
np.arange(-2, 2, 0.5))
u = -1 - x**2 + y
v = 1 + x - y**2
w = 1 - z + y
fig = ipv.figure()
ipv.quiver(x, y, z, u, v, w)
ipv.show()
Output:
This code creates a 3D quiver plot representing a vector field. The u, v, and w variables define the vector components at each point in the 3D space.
Customize Plot Appearance
Change Colors and Colormaps
You can modify the color of your plots using the color parameter:
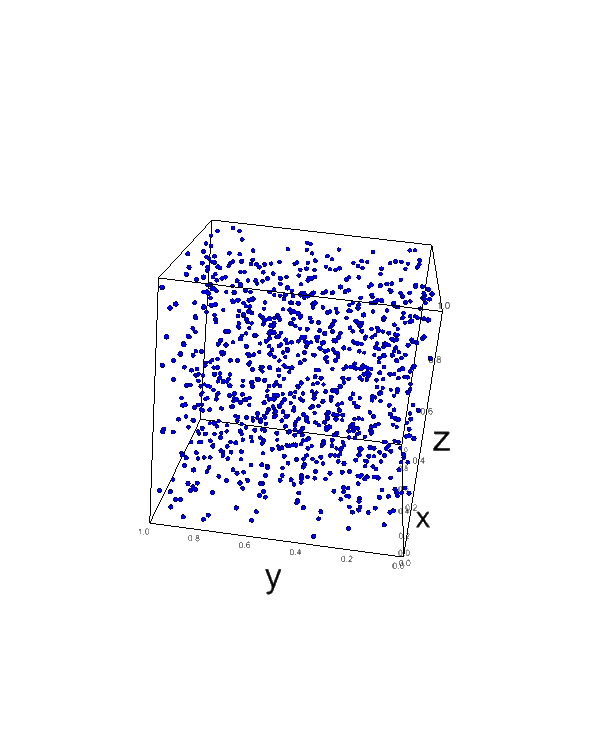
x, y, z = np.random.random((3, 1000)) c = x + y + z fig = ipv.figure() ipv.scatter(x, y, z, c=c, marker='sphere', size=2, color='blue') ipv.show()
Output:
Customize Marker Types and Sizes
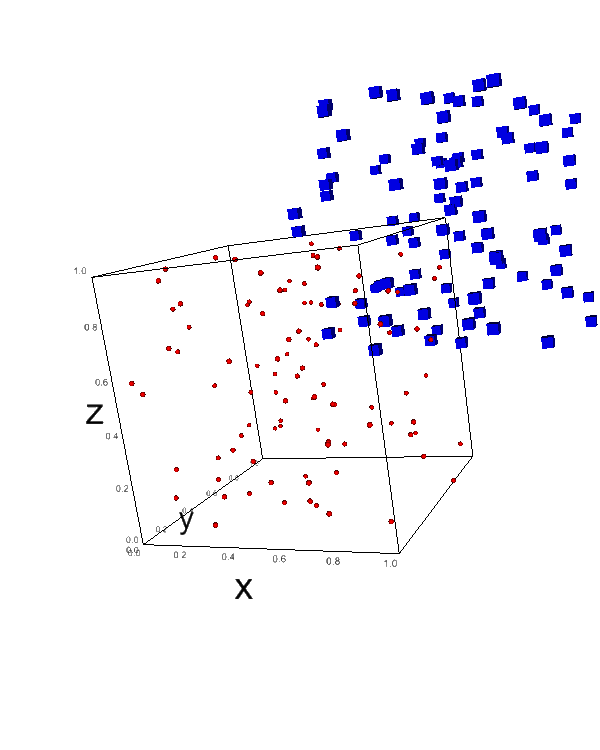
You can change the marker type and size in scatter plots using markerand size parameters:
x, y, z = np.random.random((3, 100)) fig = ipv.figure() ipv.scatter(x, y, z, marker='sphere', size=2, color='red') ipv.scatter(x + 0.5, y + 0.5, z + 0.5, marker='box', size=4, color='blue') ipv.show()
Output:
This code creates two scatter plots with different marker types (spheres and boxes) and sizes.
Mokhtar is the founder of LikeGeeks.com. He is a seasoned technologist and accomplished author, with expertise in Linux system administration and Python development. Since 2010, Mokhtar has built an impressive career, transitioning from system administration to Python development in 2015. His work spans large corporations to freelance clients around the globe. Alongside his technical work, Mokhtar has authored some insightful books in his field. Known for his innovative solutions, meticulous attention to detail, and high-quality work, Mokhtar continually seeks new challenges within the dynamic field of technology.