Create 3D Mesh Plots in Python using Matplotlib
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create various 3D mesh plots using Matplotlib, from simple triangular meshes to complex mathematical surfaces.
We’ll discover how to plot surfaces like Mobius strips and Klein bottles.
Triangular Mesh Plot
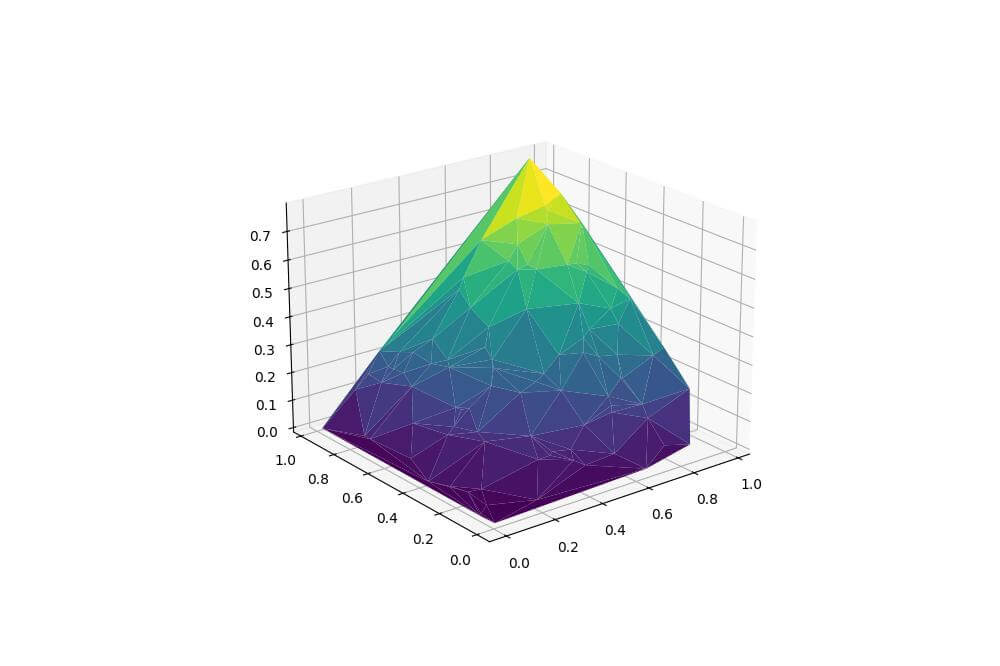
To create a basic triangular mesh plot, you can use the plot_trisurf() function:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = np.random.rand(100) y = np.random.rand(100) z = np.sin(x*y) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.plot_trisurf(x, y, z, cmap='viridis') plt.show()
Output:
This code generates a 3D surface plot using randomly generated x and y coordinates, with z values calculated as the sine of their product.
Mobius Strip Plot
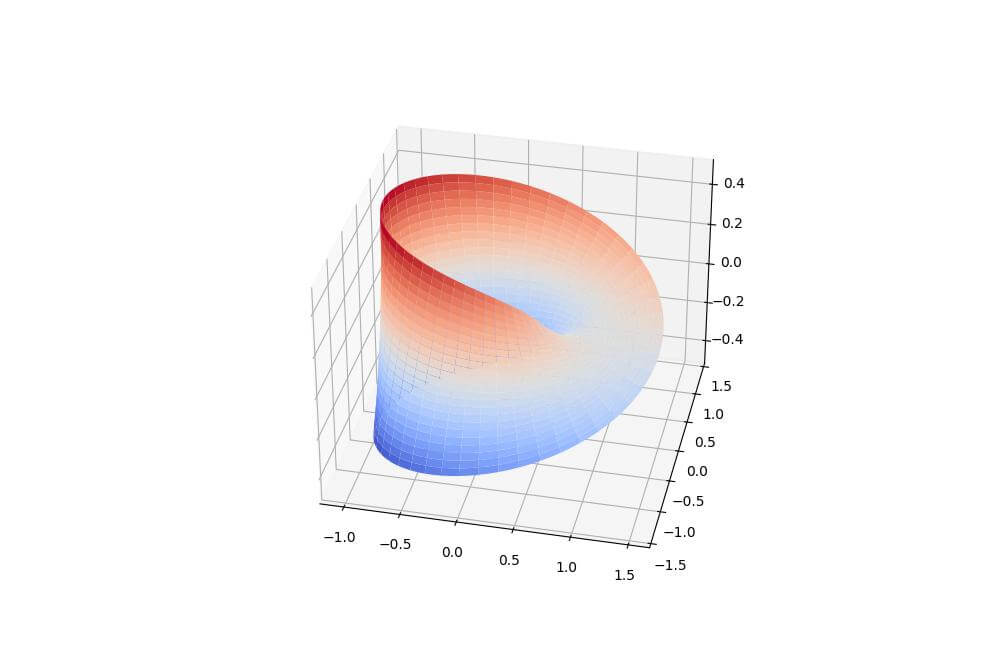
To visualize a Mobius strip, use parametric equations and plot_surface():
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt u = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) v = np.linspace(-1, 1, 25) u, v = np.meshgrid(u, v) x = (1 + 0.5*v*np.cos(u/2))*np.cos(u) y = (1 + 0.5*v*np.cos(u/2))*np.sin(u) z = 0.5*v*np.sin(u/2) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, cmap='coolwarm') plt.show()
Output:
This code generates a Mobius strip, a surface with only one side and one boundary.
Klein Bottle Visualization
You can create a Klein bottle visualization using parametric equations:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt u = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) v = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) u, v = np.meshgrid(u, v) x = (2 + np.cos(v/2)*np.sin(u) - np.sin(v/2)*np.sin(2*u))*np.cos(v) y = (2 + np.cos(v/2)*np.sin(u) - np.sin(v/2)*np.sin(2*u))*np.sin(v) z = np.sin(v/2)*np.sin(u) + np.cos(v/2)*np.sin(2*u) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, cmap='viridis', alpha=0.7) plt.show()
Output:
This code creates a 3D representation of a Klein bottle, a non-orientable surface that doesn’t have an inside or outside.
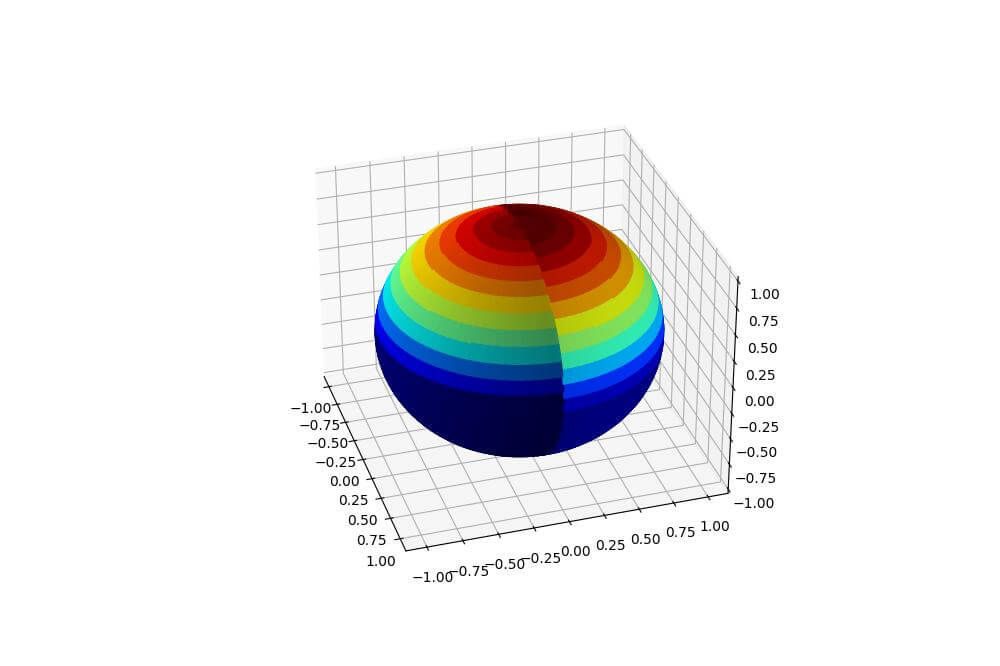
Sphere with Custom Coloring
You can create a sphere with custom coloring using plot_surface():
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt phi = np.linspace(0, np.pi, 100) theta = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) x = np.outer(np.sin(theta), np.cos(phi)) y = np.outer(np.sin(theta), np.sin(phi)) z = np.outer(np.cos(theta), np.ones_like(phi)) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, facecolors=plt.cm.jet(z)) plt.show()
Output:
This code generates a sphere with custom coloring based on the z-coordinate.
The resulting plot displays a vibrant sphere with colors transitioning from blue at the bottom to red at the top.
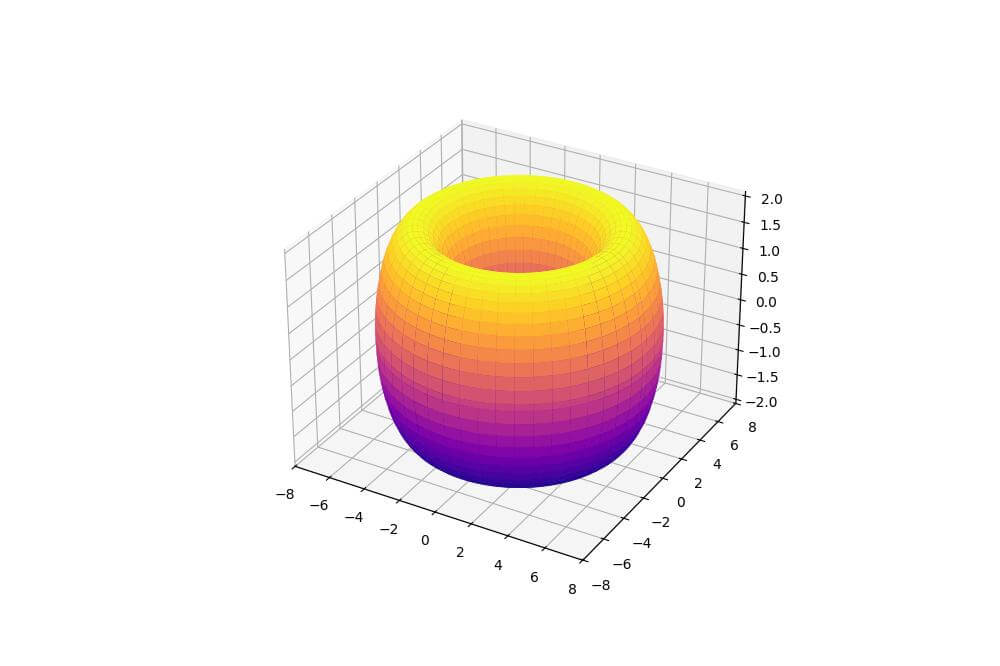
Torus Plot
You can create a torus plot using parametric equations:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt R, r = 5, 2 u = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) v = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) u, v = np.meshgrid(u, v) x = (R + r*np.cos(v)) * np.cos(u) y = (R + r*np.cos(v)) * np.sin(u) z = r * np.sin(v) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, cmap='plasma') plt.show()
Output:
This code generates a torus with a donut-shaped surface.
The resulting plot shows the distinctive shape of the torus with a smooth color gradient.
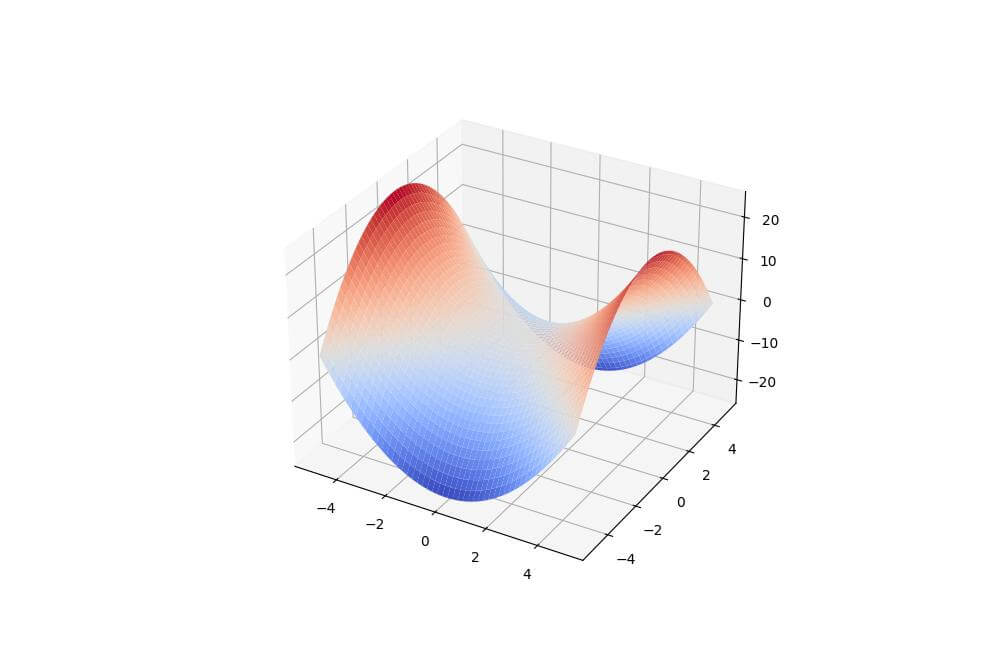
Saddle Surface Plot
Visualize a saddle surface using the plot_surface() function:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100) y = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100) x, y = np.meshgrid(x, y) z = x**2 - y**2 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, cmap='coolwarm') plt.show()
Output:
This code creates a saddle surface, which has a distinctive shape that curves up in one direction and down in the perpendicular direction.
The resulting plot shows the saddle-like curvature of the surface.
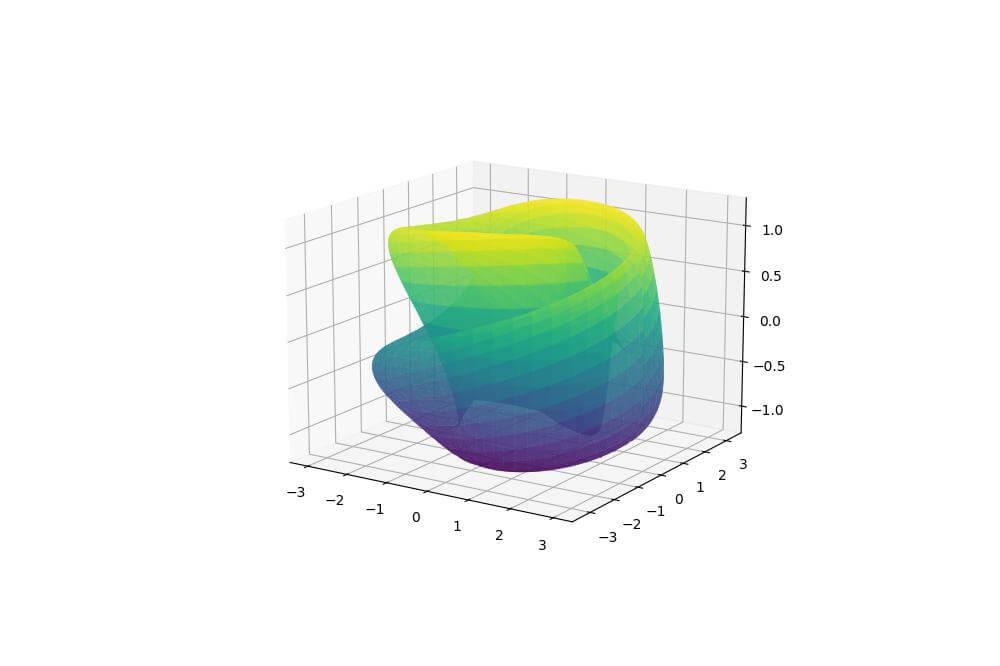
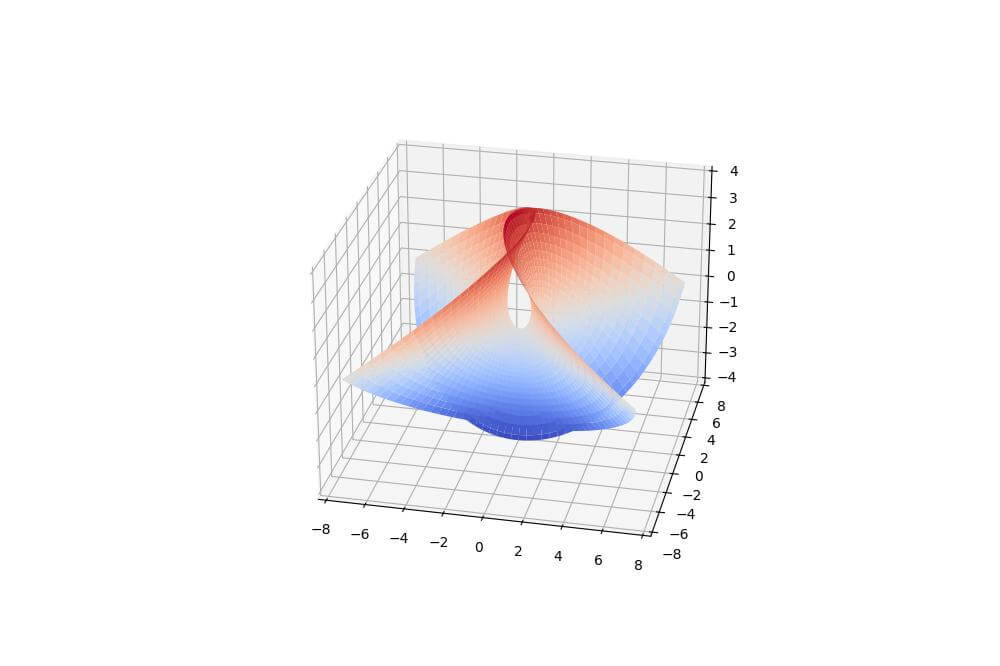
Enneper Surface Plot
You can visualize an Enneper surface using parametric equations:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt u = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100) v = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100) u, v = np.meshgrid(u, v) x = u - u**3/3 + u*v**2 y = v - v**3/3 + v*u**2 z = u**2 - v**2 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, cmap='coolwarm') plt.show()
Output:
This code generates an Enneper surface with a self-intersecting minimal surface.
The resulting plot shows the complex, twisted nature of the Enneper surface with its characteristic shape.
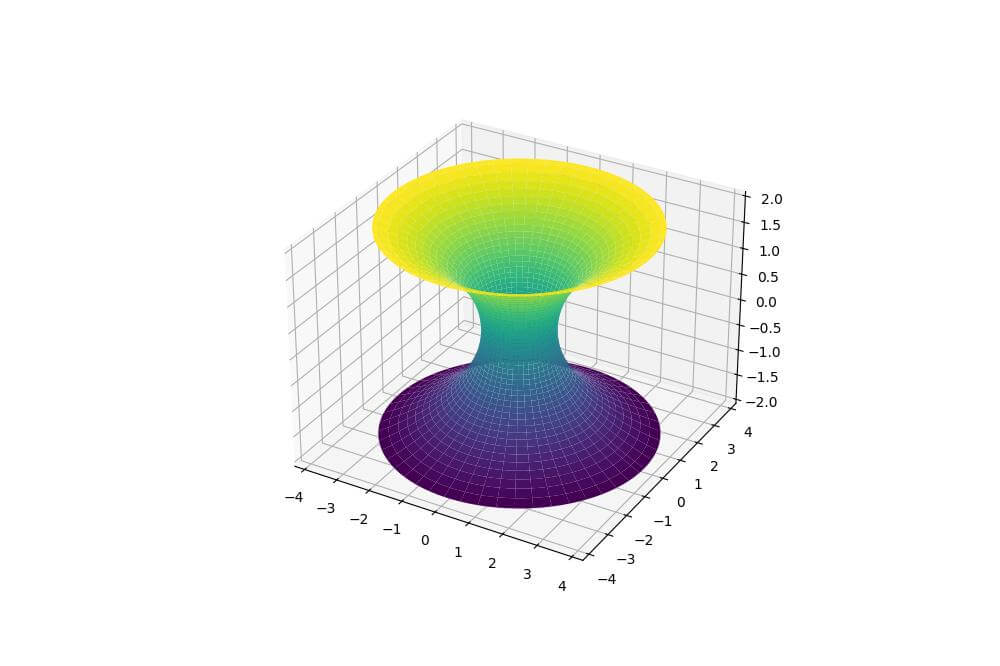
Catenoid Surface Plot
You can create a catenoid surface using hyperbolic cosine function by rotating a catenary curve around an axis:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt u = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100) v = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) u, v = np.meshgrid(u, v) x = np.cosh(u) * np.cos(v) y = np.cosh(u) * np.sin(v) z = u fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, cmap='viridis') plt.show()
Output:
Helicoid Surface Plot
You can visualize a helicoid surface using parametric equations:
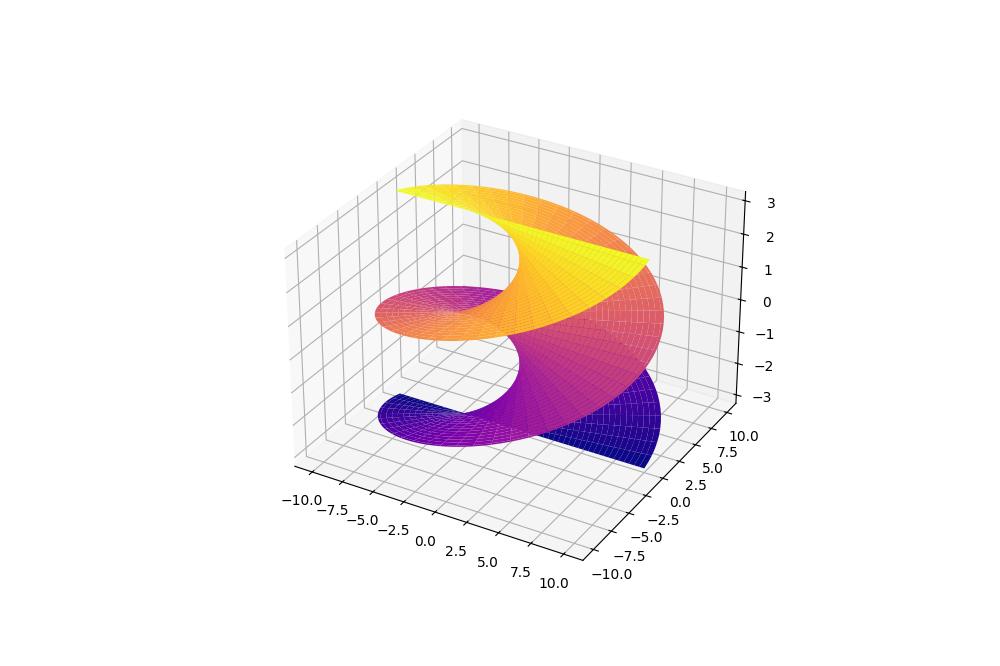
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt u = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100) v = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 100) u, v = np.meshgrid(u, v) x = u * np.cos(v) y = u * np.sin(v) z = v fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, cmap='plasma') plt.show()
Output:
This code creates a helicoid, a ruled surface that resembles a screw or a spiral staircase.
Mokhtar is the founder of LikeGeeks.com. He is a seasoned technologist and accomplished author, with expertise in Linux system administration and Python development. Since 2010, Mokhtar has built an impressive career, transitioning from system administration to Python development in 2015. His work spans large corporations to freelance clients around the globe. Alongside his technical work, Mokhtar has authored some insightful books in his field. Known for his innovative solutions, meticulous attention to detail, and high-quality work, Mokhtar continually seeks new challenges within the dynamic field of technology.